This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license.
Authors:
(1) Falke B. Ø. Carlsen, Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark & [email protected];
(2) Lars Bo P. Frydenskov, Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark & [email protected];
(3) Nicolaj Ø. Jensen, Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark & [email protected];
(4) Jener Rasmussen, [email protected];
(5) Mathias M. Sørensen, [email protected];
(6) Asger G. Weirsøe, [email protected];
(7) Mathias C. Jensen, Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark & [email protected];
(8) Kim G. Larsen, Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark & [email protected].
Table of Links
2 Definitions
We recall the definitions of concurrent games and alternating-time temporal logic.

A computation starting in the state q is called a q-computation.

Alternating-time Temporal Logic The alternating-time temporal logic (ATL) [1] is defined with respect to a finite set Π of propositions and a finite set Σ = {1,...,k} of players. An ATL formula is given by the abstract syntax:
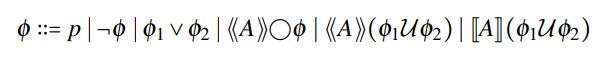
where p ∈ Π is a proposition and A ⊆ Σ is a set of players. The operators ⟪⋅⟫ and J⋅K are path quantifiers. We will refer to them as "enforce" and "despite", respectively. The ◯ ("next") and U ("until") are temporal operators. Additional temporal operators like ♢ ("eventually") and □ ("invariant") are derived as usual.
Given a state q of a game structure S, we write q ⊧ φ to indicate that the state q satisfies the property described by φ. The satisfactory relation ⊧ is defined inductively:

This paper is available on

